People hate dealing with slow sites, and in general, slow sites frustrate many users. Nowadays, with the latest communications technologies, such as 5G and fiber-optic internet, People are increasingly used to super-fast internet, even on their cell phones. Statistics show that 53% of users won’t wait more than 3 seconds for a website to load 1, and a slow site means less conversion, and less conversion means fewer sales 2.
Let’s look at a slow site from a different angle: “Environmental effect.” Yes, it might be surprising, but slow sites contribute to more greenhouse gas emissions. This is because a slow site requires more energy to serve the user 3.
You can check your website’s carbon emission rate using this tool: websitecarbon.com.
Did you know that You can check your website’s carbon emission rate using this tool: websitecarbon.com.
Almost half of the sites are powered by WordPress (43.3% ) 4. That means if only WordPress sites could decrease their loading time, users would sense faster internet almost 50% of the time.
Website load time is among the 3 Google’s core web vitals metrics (namely Largest Contentful Paint, Interaction To Next Paint and Cumulative Layout Shift in order measuring loading performance, responsiveness and visual stability.) Google says a good core web vitals score can lead to a better user experience which is in line with what Google’s core ranking systems seek to reward 5. All that means is that website speed can have a positive effect on the website’s rankings.
A few different factors play a crucial role in achieving a fast-loading WordPress site, including:
- Hosting Performance,
- Content/Resources Optimization,
- Caching
- Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Premium DNS
In this blog post, I will cover how each of these factors can enhance the load time of a WordPress site and show you how you can achieve a super fast website by hosting your site on a premium Managed WordPress hosting like Couldways, tweaking it a bit, and using Cloudways WordPress Cache plugin “Breeze.” Let’s get started!
Let’s first see what Cloudways is and what problem it solves.
What is Cloudways
Cloudways is a managed cloud hosting platform; it does not provide its own hosting infrastructure. Instead, it integrates with several major cloud hosting platforms, including DigitalOcean, Vultr, Google Cloud Platform, AWS (Amazon Web Services), and Linode. Cloudways lets you launch projects with different applications, such as WordPress, WooCommerce, Magento, PHP, and Laravel.
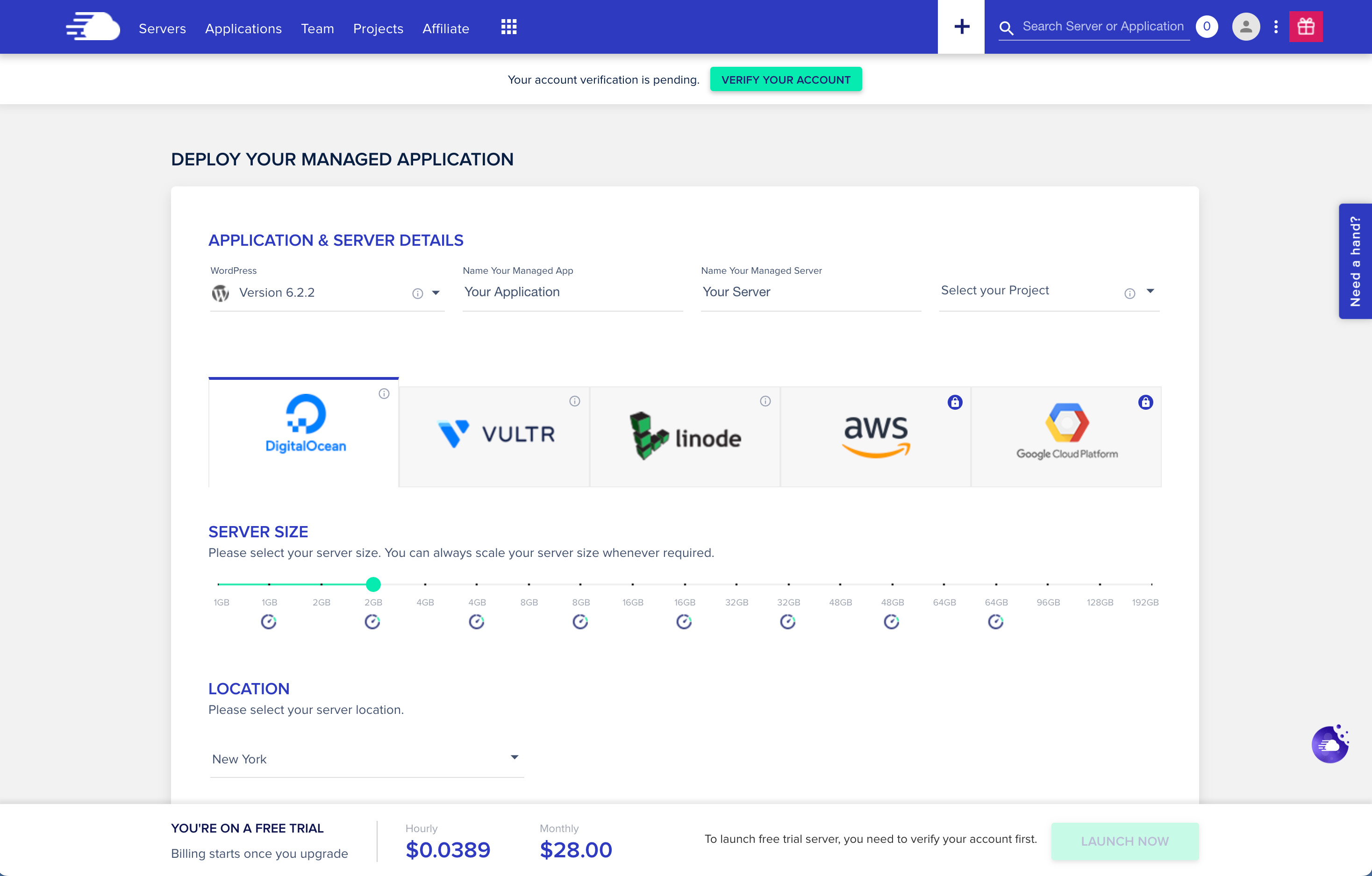
Cloudways’ main value creation circles around addressing technical complexity, performance, and security issues that come with managing one’s own cloud hosting by offering:
- Simplified Cloud Hosting Management: Cloudways provides a platform that simplifies the deployment, management, and scaling of web applications on major cloud providers, removing the complexities associated with server management.
- Performance Optimization: The platform includes features such as built-in caching, CDN integration, and optimized server stacks to ensure fast and reliable website performance.
- Enhanced Security: Cloudways offers robust security measures, including automated backups, dedicated firewalls, SSL integration, and regular security patches.
Cloudways, with over 100K users, features a clean, intuitive interface that reduces the complexities of managing cloud infrastructure. Its competitive pay-as-you-go pricing model, the option to choose from multiple cloud providers, and simplified deployment/management of different web applications and e-commerce platforms not only get the job done but also reduce the cost and risk associated with running your own cloud hosting.
Now, let’s see how a WordPress site’s speed is affected by different factors; I will also show you how Cloudways can help you speed up your site for each one.
Hosting Performance
It might not be very evident for non-technical users how hosting can affect a website’s load time. You might have tried everything but still experience a huge initial server response time. I was there, too. Let me tell you something: during many years of optimizing WordPress sites, I could significantly increase websites’ load time by just moving them to a better hosting provider.
Now, let’s get back to technicalities. Let’s see how a hosting performance can impact a website’s load time. Here are the 3 main ways:
- Server Resources Limitations: A server with a higher number of CPUs, RAM, and SSD storage will be able to process requests faster, making a site hosted on it load much faster.
- Server’s Datacenter Location: A server that is served from a datacenter that is located closer to the user, pulling up the site can lead to sensing a faster site for that user.
- Server’s Scalability: Servers that can better manage higher bandwidth and fluctuating traffic volumes prevent bottlenecks, leading to faster load times and improved reliability.
Cloudways Managed WordPress hosting uses SSD storage, which can significantly improve website loading speeds compared to traditional HDD storage offered in some plans by other providers.
Content/Resources Optimization
Content/Resource optimization can be achieved by using performance optimization plugins such as Perfmatters, WP Rocket, Autoptimize, WP-Optimize, W3 Total Cache, and Cloudways Breeze plugin. These plugins enhance website speed and efficiency through various techniques:
- Compression: Reducing the size of HTML, CSS, and JS files to decrease load times. This is often achieved through Gzip compression, which minimizes the amount of data transferred between the server and the user.
- Browser Caching: Storing static versions of your website to serve users quickly without repeatedly generating the same content dynamically. This reduces server load and speeds up page delivery.
- Minification: Removing unnecessary characters (e.g., spaces, comments) from code files to reduce their size. This helps in faster loading and execution of scripts and styles.
- Database Optimization: Cleaning up and optimizing your database by removing unnecessary data, such as old revisions, spam comments, and transient options, which can bloat the database and slow down your site.
- Lazy Loading: Delaying the loading of images and other media until they are actually needed (i.e. when they appear in the user’s viewport). This reduces the page’s initial load time.
- Defer JavaScript: Delaying the loading of JavaScript files until after the entire HTML document has been parsed and loaded. This allows the page to become interactive more quickly.
- Delay JavaScript: Involves postponing the execution of JavaScript until certain conditions are met using setTimeout, setInterval, or event listeners that wait for user interaction. This technique is often used to prevent JavaScript from blocking the initial rendering of the page, which can improve perceived load times.
- Critical CSS: Loading essential CSS required for the initial render directly in the HTML code. This ensures that the content is styled as quickly as possible, improving the perceived load time.
- Removing Unused CSS: By identifying and eliminating unused CSS, the overall file size is reduced, resulting in faster loading times. This can be done using tools and plugins designed to analyze and clean up CSS.
- Optimizing Images: Use tools like Imagify or Smush to compress images without losing quality. This reduces the load on your CDN and speeds up your site.
- Preloading: Instructs the browser to prefetch and cache resources (such as images, fonts, scripts, stylesheets, and even other pages) before they are actually needed to help reduce load time and latency.
Using the Cloudways Breeze WordPress Cache plugin, you can perform the following performance optimizations:
File Optimization: It minifies HTML, CSS, and JS files by removing white spaces and comments from them. It also has options to combine CSS and JS files and to exclude certain files from being merged or minified.
Preloading: Preloading fonts and links and prefetching DNS records.
Database Optimization: Breeze database optimization lets you clean up your WordPress database by removing unnecessary or orphaned tables, fields, and records.
CDN and Varnish settings can also be set via the Cloudways Breeze WordPress plugin.
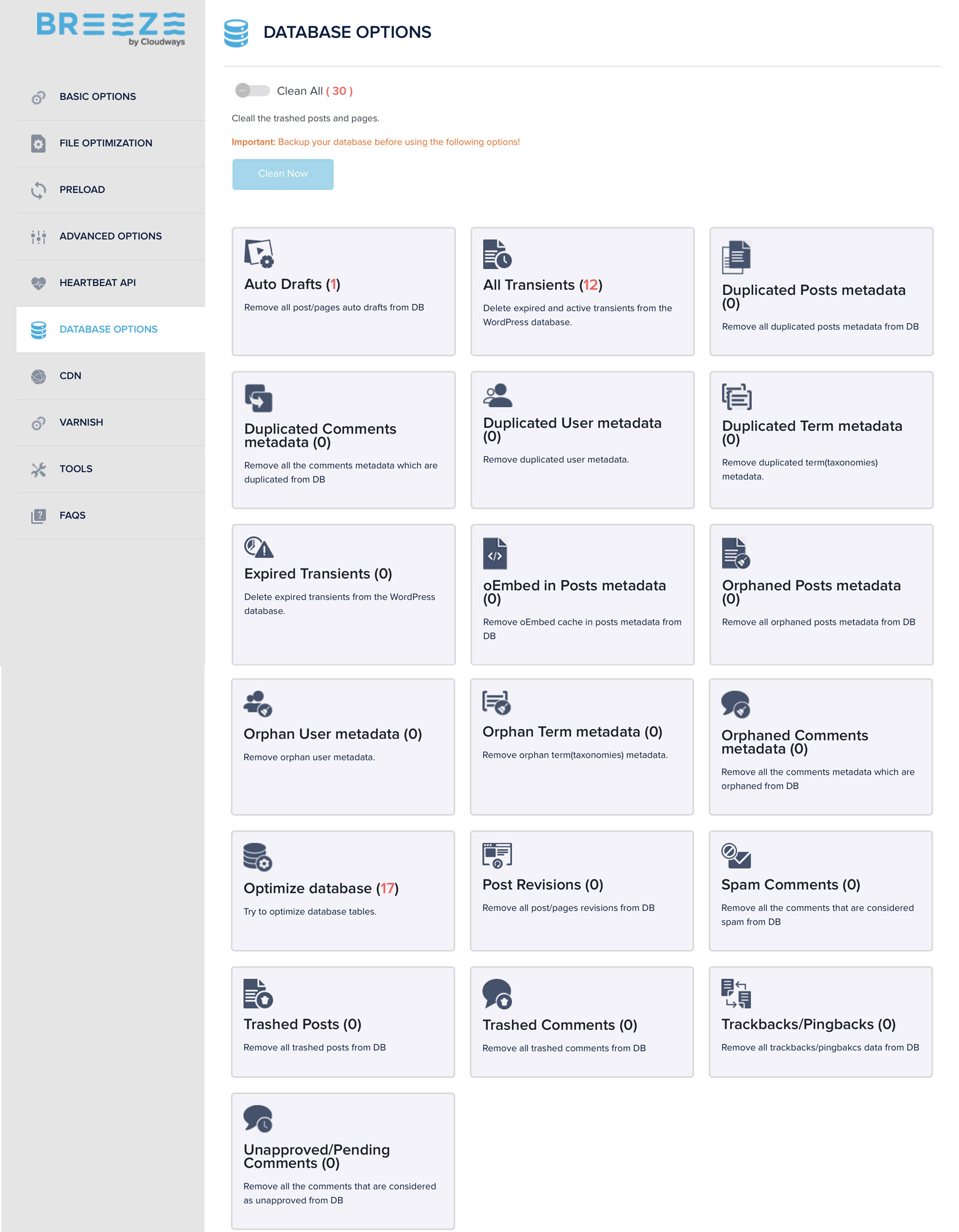
Cloudways Breeze is relatively new and has fewer optimization options compared to other mainstream WordPress performance plugins, such as WP Rocket or Perfmatters, but if you host your WordPress site on Cloudways, you might want to use Breeze for smoother and better integration with the Cloudways features.
Test and Monitor: Regularly test your site’s speed using tools like GTmetrix or Google PageSpeed Insights. Monitor your site’s performance optimization plugin settings as needed.
Caching and its Different Levels: Hosting, DNS, and Browser
Caching is an important technique that is used to help with a website’s performance. It works by storing copies of files or data in easily accessible locations rather than fetching them again from sources far away, resulting in speeding up load times and reducing processing times. Caching can be implemented at hosting, DNS, and browser:
From the location perspective, caching can come down to two types: client-side caching and server-side caching. Client-side caching is when the already downloaded resources of a page are kept in the user’s browser and served from the local storage of the user when the browser wants to load those resources again. In comparison, server-side caching means storing the result of the server’s time-consuming processes so that if the same processes are requested again, it can be just served from the server cache instead of repeating those processes again.
1. Hosting-Level Caching
Hosting-level caching is a server-side caching that involves storing copies of website data on the server to quickly deliver to users. This type of caching can significantly reduce load times by minimizing the need to generate pages dynamically for every request.
Hosting-level caching can by itself be divided into page caching, object caching, and code caching, with page caching being as storing the entire page in the server-side cache storage and object caching being as storing the the result of the same processes, either be database query or an API call, in the server’s hard disk and code execution caching being as storing the compiled or executable form of code to avoid the overhead of recompiling or interpreting the source code every time it is run.
Types of Hosting-Level Caching
- Page Caching: Stores entire HTML pages generated by the server. When a user requests a page, the cached version is delivered instead of generating it again.
- Object Caching: Caches database/API query results. This is particularly useful for reducing database load and speeding up response times for dynamic content.
- Code Caching: Code execution caching is a technique used by different programming languages to minimize the server’s CPU during code execution by caching the result of the executable codes.
Varnish and Redis
Many managed WordPress hosting providers, such as Cloudways, implement server-side caching solutions like Varnish and Redis to speed up websites.
Varnish 6 is a reverse proxy caching or HTTP caching, which is a type of page caching. It works by caching the result of the HTPP request on a proxy server, so when the same request is made again, it is served from the reverse proxy instead of the main server. This speeds up the process and reduces the main server load. Varnish has three important benefits:
- It loads cached content, which speeds up the process.
- It reduces the server’s load as the request is only forwarded to the main server if it does not exist in the proxy server.
- It reduces the latency by serving the content from a location closer to the user.
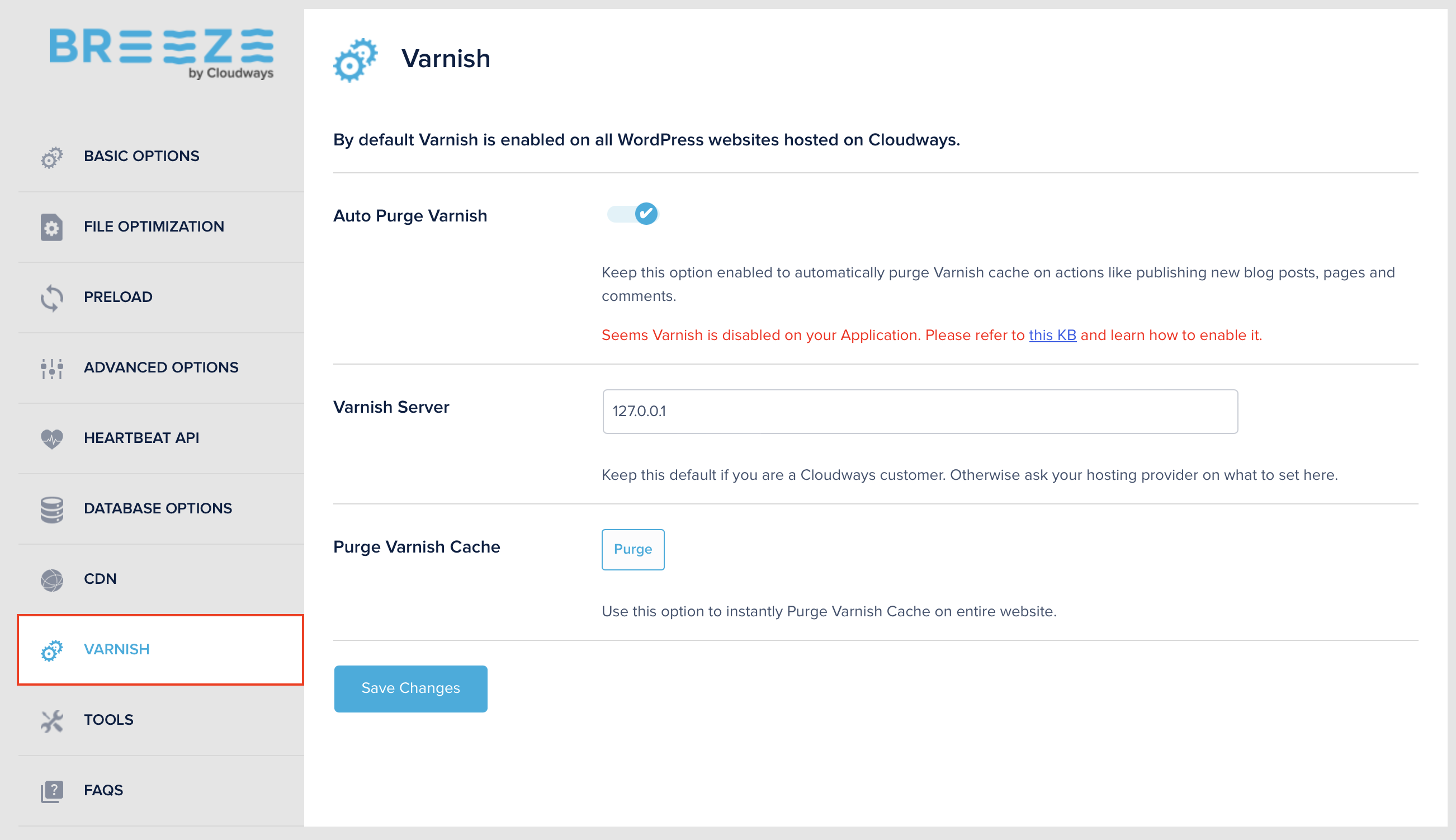
On the other hand, Redis 7 is an object caching technique in which it stores results of frequently accessed data such as database queries, API queries, or session data in memory which indeed helps reduce the time necessary to access these data again.
Code Caching
Now let’s see what different programming languages offer as for code execution caching:
- PHP
- Opcode Caching is a performance enhancing extension for PHP. It Caches the compiled bytecode of php scripts to avoid recompiling them for every request, which can enhance performance for PHP-based websites like WordPress.
- Java
- Just-In-Time (JIT) Compilation: In Java, the JVM (Java Virtual Machine) uses JIT compilation to convert Java bytecode into native machine code at runtime. The JIT compiler stores the native code, similar to how opcode caching works in PHP, to speed up execution for future calls. Java also uses Class Data Sharing which is just another caching strategy particularly used to store and share the internal representation of classes, reducing startup time.
- Python
- pyc Files: Python compiles .py files to .pyc files, which are cached versions of the bytecode. These .pyc files are in a pycache directory and are used to execute the program, bypassing the need to recompile the source code each time by reusing the bytecode.
- .NET Languages
- Native Image Generation (NGEN): In .NET, the NGEN tool precompiles bytecode into native code and stores it in the native image cache. This precompiled code is used for execution, reducing the need for just-in-time compilation and improving startup times.
- JavaScript
- V8 Engine: The V8 JavaScript engine used by Chrome and Node.js compiles JavaScript to native machine code. The V8 engine uses various caching strategies, including caching compiled code to speed up subsequent executions.
2. DNS-Level Caching
DNS-level caching involves storing DNS query results to quickly resolve domain names without querying the DNS server each time. This can significantly speed up the process of connecting to websites.
If you use the Cloudways DNS Made Easy add-on or integrate it with your Cloudflare account to manage your DNS records for you, you benefit from cached DNS that is served from a global network of data centers, improving load times by reducing initial DNS lookup time.
3. Browser Caching
Browser caching involves storing website resources (e.g., images, CSS, JavaScript) locally in the user’s browser. This allows faster loading of previously visited websites by avoiding the need to download the same resources again.
How to Enable Browser Caching?
Browser caching is set via the page’s HTTP headers. Header settings such as Cache-Control, Expires, and ETag control browser caching behavior. These headers specify how long resources should be cached and when they need to be revalidated.
- Cache-Control: Provides detailed instructions on how to cache the resource, specifying directives like
max-age,no-cache,no-store,public, andprivate. - Expires: Sets an expiration date and time for the resource, after which it is considered stale and must be revalidated.
- ETag: Uses a unique identifier for resource versioning, allowing the server to determine if a cached resource is still valid or needs to be refreshed.
For a WordPress site, you can manually set these HTTP headers via the .htaccess file, or you can use caching plugins like Breeze, WP Rocket, and W3 Total Cache to do it for you.
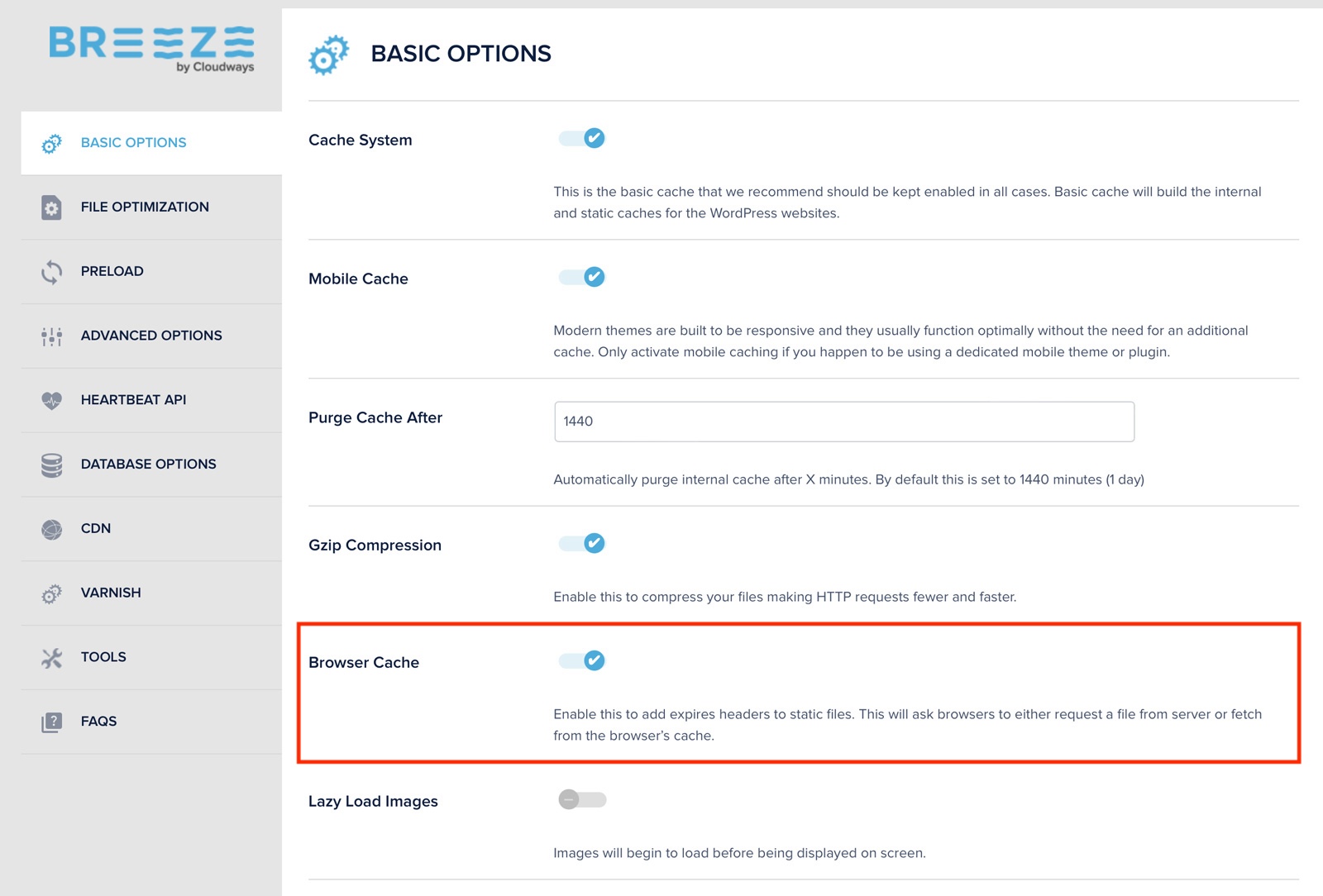
Here is how you can enable browser caching using the Cloudways Breeze WordPress plugin using the following steps:
- Install and activate the Breeze WordPress Cache Plugin like any other WordPress plugin you install.
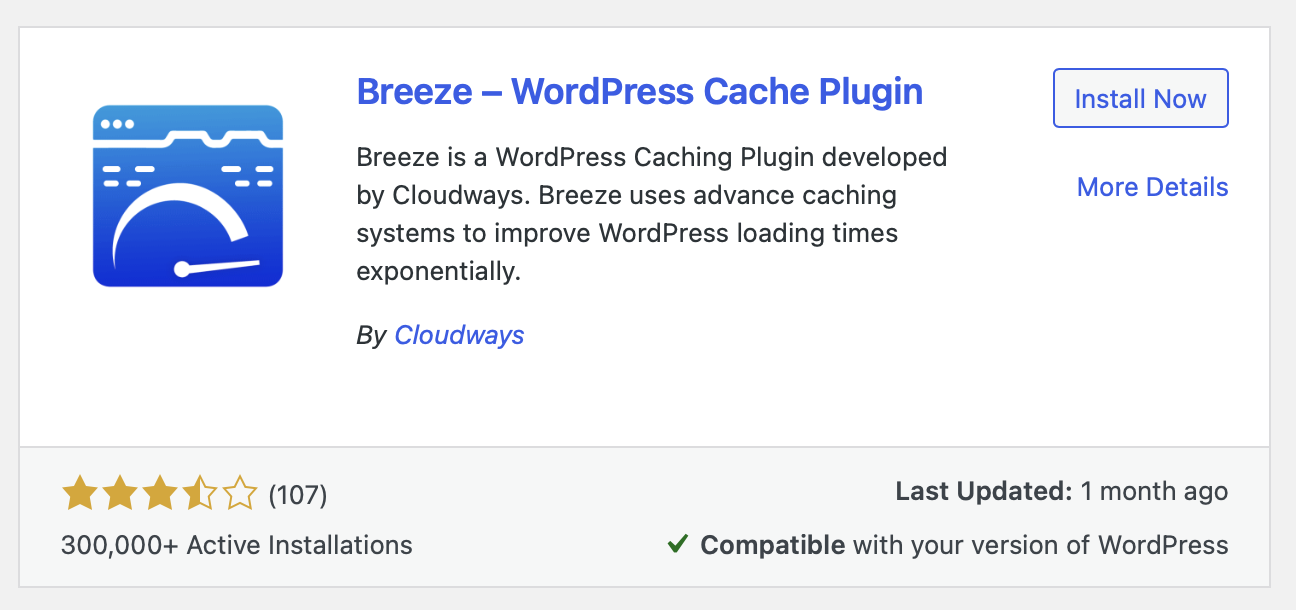
- Then, navigate to the plugin’s Settings page and enable the Browser Cache option.
Content Delivery Network
Content Delivery Network or CDN, the name might remind you of a supply chain kind of network, right? It is indeed a kind of supply chain network for but websites. The way it works is that it helps you bring your site closer to the user’s location instead of having the user travel all the way to your warehouse (in our case, where your site’s hosting data center is located). In other words, it is like a network of mini-warehouses (CDN servers) spread all around the world, where users are served your content from the closest location.
So, your static files, such as images, stylesheets, and Javascript files, can be served from different locations depending on where the user browsing your site is located. This helps reduce the latency and increase the website’s lead time.
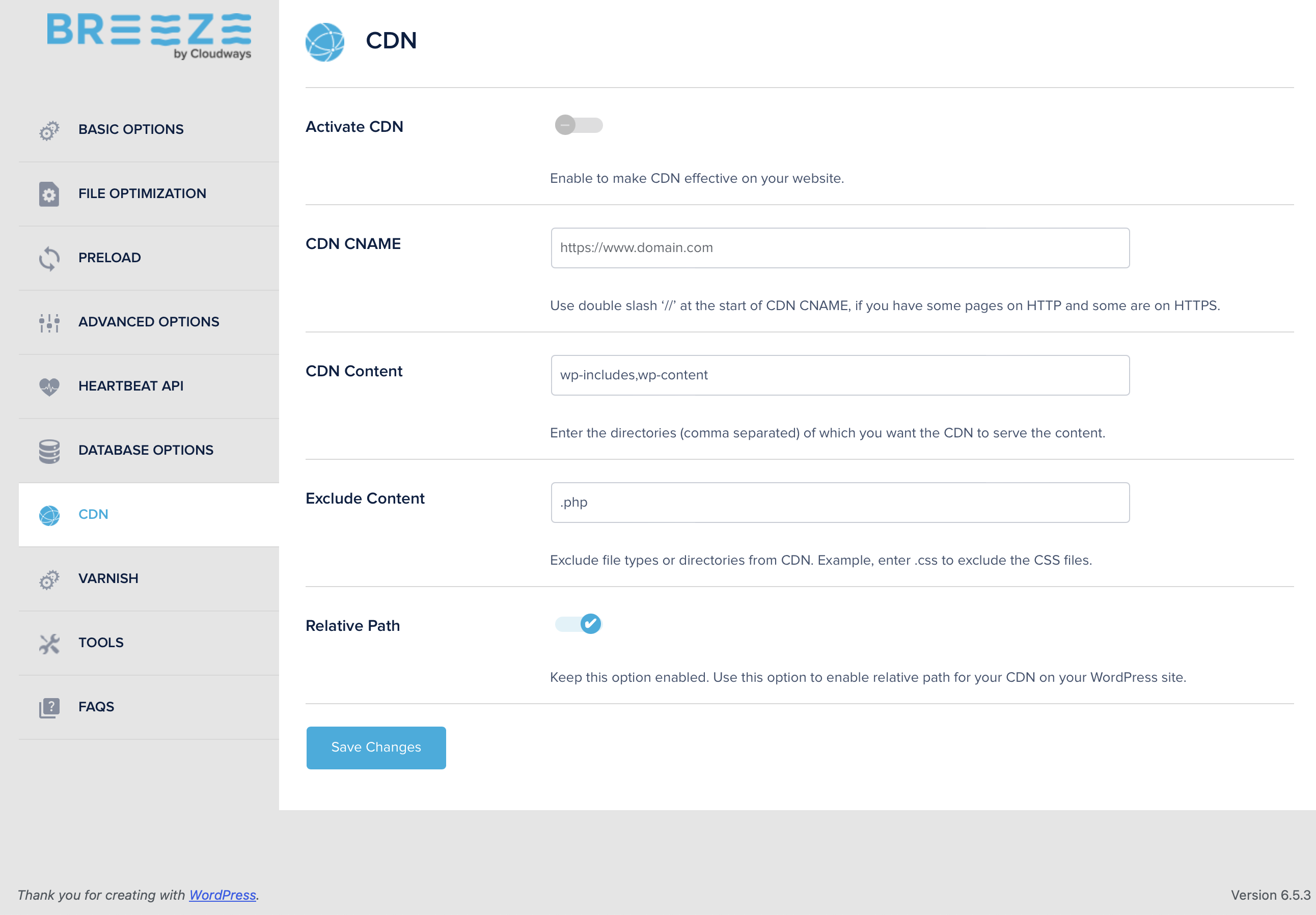
Now, let’s take the example of CloudWays. With CloudWays, you can set up CDN integration like a breeze:
- Sign Up for a CDN Service: Cloudways partners with StackPath and other CDN providers. Choose one that fits your needs.
- Enable the CDN: In your Cloudways dashboard, go to the “CDN” tab and enter your CDN URL.
- Configure Your Site: Use plugins like Breeze to integrate the CDN with your WordPress site.
Premium DNS
We have already covered the effect of DNS on a website’s load time, specifically when it comes to the initial connection time in the DNS caching section. Premium DNS services such as Cloudflare, Google Cloud DNS, and Amazon Route 53 operate on the same principle: they provide a cached version of the DNS directory so that they can quickly resolve the domain name to the IP address. However, Premium DNS services offer additional features and enhancements that can significantly improve website performance, reliability, and security.
Benefits of Premium DNS Services
- Enhanced Performance:
- Global Anycast Network: Premium DNS services use a global Anycast network, which means DNS queries are routed to the nearest DNS server in the network. This reduces latency and speeds up the DNS resolution process.
- Reduced Latency: With multiple points of presence (PoPs) around the world, Premium DNS services minimize the distance between the user and the DNS server, ensuring faster response times.
- Improved Reliability:
- Redundancy and Failover: Premium DNS providers offer built-in redundancy and failover mechanisms. If one server fails, queries are automatically redirected to another server, ensuring continuous availability.
- High Availability: These services are designed to be highly available, with uptime guarantees often backed by Service Level Agreements (SLAs).
- Increased Security:
- DDoS Protection: Premium DNS services often include robust DDoS protection, safeguarding your DNS infrastructure from volumetric attacks that could otherwise take your site offline.
- DNSSEC: DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC) add a layer of security to your DNS by preventing attacks such as DNS spoofing and cache poisoning.
- Advanced Management Features:
- Traffic Management: Some Premium DNS services offer advanced traffic management features, such as load balancing and geolocation-based routing, which can optimize the delivery of content based on user location.
- Monitoring and Analytics: Comprehensive monitoring and analytics tools provide insights into DNS query patterns and help identify and mitigate potential issues.
Although Cloudways does not offer its own branded Premium DNS, it supports robust DNS solutions through an add-on, DNS Made Easy 8, as well as integrations with premium DNS services such as Cloudflare.
DNS Made Easy offers features like instant propagation, high query quotas, enhancing DNS lookup performance and reliability by caching DNS records, and providing quick domain resolution.
Cloudways can also integrate with Cloudflare, providing options like Cloudflare Enterprise.
- https://www.thinkwithgoogle.com/consumer-insights/consumer-trends/mobile-site-load-time-statistics/ ↩︎
- https://www.thinkwithgoogle.com/marketing-strategies/app-and-mobile/load-time-to-conversion-statistics/ ↩︎
- https://nitropack.io/blog/post/slow-websites-carbon-footprint ↩︎
- https://w3techs.com/technologies/details/cm-wordpress ↩︎
- https://developers.google.com/search/docs/appearance/core-web-vitals ↩︎
- https://varnish-cache.org ↩︎
- https://redis.io ↩︎
- https://www.cloudways.com/en/dns-made-easy.php ↩︎

