Nowadays, people like a website with proper security. Even Google, the number 1 search engine, considers SSL/TLS certificate as a ranking factor.
In the world of website security, two of the most popular options for obtaining and managing SSL certificates are ZeroSSL and Let’s Encrypt.
Both offer free, automated SSL certificate issuance and renewal, but there are some key differences to consider when choosing between the two.
| Feature | Let’s Encrypt | ZeroSSL |
| Certificate Authority (CA) | Certificate Authority (CA) | Certificate Authority (CA) |
| Certificate Type | Domain Validation (DV) | Domain Validation (DV) |
| Website | https://letsencrypt.org | https://zerossl.com |
| Launch | 2014 / 2015 | 2016 |
| Funding | Sponsorships & Donations (Non-profit) | Subscription (Paid Plans) |
| Certificate Issuing | ACME only | Online, ACME, REST API |
| Price | Free | Free / Paid |
| Certificate Validity | 90 days | 90 days / 1 year |
| Domain Verification | DNS, File Upload | DNS, File Upload, Email |
| Rate Limit | 50 Certificates per Week/Domain | No Limit / Specific Limit (per plan) |
| Multi-Domain Certificates | Supported | Supported (per plan) |
| Wildcard Certificates | Supported | Supported |
| Technical Support | Not Available | Available (per plan) |
| ACME Automation | Supported | Supported |
| Remote API | Not Available | Available (per plan) |
| User Interface | Not Available | Available |
Zero SSL Overview

ZeroSSL launched in 2016 on a mission to make SSL certificates available for everybody on the web. The tech world considers this the best alternative to Let’s Encrypt as a free SSL provider.
According to their data, they provide over 1 million SSL/TLS certificates for websites every month. Initially, these companies used to provide free SSL through a third-party vendor. As the company grew over time, it became a standalone TLS/SSL certificate authority to provide and validate the SSL certificate.
ZeroSSL still provides 90-day free SSL, but they have paid plans as the company needs more funding. Also, you will get some unique features in the premium plans, which are unavailable in the free SSL.
ZeroSSL acquired SSL For Free, another free SSL provider, in May 2020 to provide better service for free users.
Let’s Encrypt Overview

Let’s Encrypt is the first project of the Internet Security Research Group (ISRG), which works for public benefit. Let’s Encrypt is a completely free and automated open certificate authority. Their goal is to maintain a privacy-respecting web in the best possible way.
Let’s Encrypt offers free digital SSL/TLS certificates to ensure HTTPS for all. HTTPS protects users’ data from hackers and identity thieves.
Let’s Encrypt provides free SSL certificates to over 300 million sites. They share their data on this stats page on their site.
If you are wondering how they are maintaining these massive data and SSL certificates free, they are getting funds from some big companies. Mozilla, Chrome, Cisco, and Amazon are some companies funding Lets Encrypt.
Before 2015, an SSL certificate was a wholly paid service. They are the first ones to introduce this HTTPS and domain validation certificate for free.
ZeroSSL vs Lets Encrypt: Point of Difference
I got the overview for both authorities. Let’s find out the difference between them at various points. I will compare the UI, certificate, price, validity, verification, and technical support.
User Interface
The user interface is the number one point when choosing any tool/website. I will start the comparison from here as this is the face of the tool.
UI: ZeroSSL
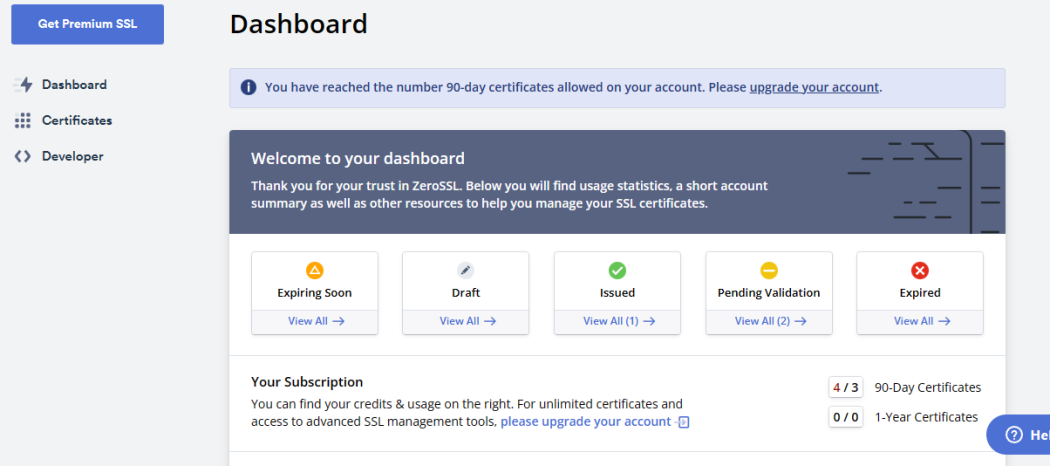
ZeroSSL has a very user-friendly UI. You can navigate to any option with just a few clicks. You can issue, renew, manage or delete a certificate from one place. Also, You can install the certificate through the inbuilt setup wizard on the site.
UI: Lets Encrypt
Being a free solution to secure HTTPS certificates, Let’s Encrypt doesn’t have any user interface for certificate management. It entirely depends on the ACME Interface to provide and manage certificates.
Verdict: ZeroSSL has a better User Interface and experience. Beginners can easily adjust to the website, and unlike Let’s Encrypt, the instructions are much easier to understand.
Issuing Certificate
Before comparing how these authorities issue certificates, let’s understand the ACME protocol.
ACME, or Automated Certificate Management Environment, is a protocol that enables the automated generation and renewal of digital certificates securely and efficiently.
It utilizes Internet protocols such as HTTPS, DNS, and TLS-ALPN for secure data exchange between domain registrars and certificate authorities.
Through this protocol, ACME can complete the issuance and renewal of certificates without manual intervention by either party.
Most hosting companies, such as Hostinger, Bluehost, Siteground, etc., use the ACME certification, so you don’t need to install the certification manually.
Certificate: Zero SSL
ZeroSSL will allow you to get HTTPS certification in 3 methods.
Certificate: Let’s Encrypt
Although you will get a free SSL certificate from Lets Encrypt, they don’t have the facility to allow a certificate from their site. The only way is to have Lets Encrypt SSL compatibility on your cPanel or use an ACME protocol tool.
You can install an ACME protocol tool on a Windows server with Win-Acme or use a Linux or Mac OS terminal. Also, you have to know if your server is Apache or Nginx. Each system has its requirement.
You must have server access to your domain to use this method.
Verdict: ZeroSSL is much easier to issue an SSL certificate than Let’s Encrypt. Also, having a UI is the best option for non-techy and beginner website owners.
Pricing
Pricing: ZeroSSL
Zero SSL has both free and paid plans. The free plan is free-forever, where you can get three certificates for 90 days, requiring renewal when it expires. You can remove the certificate and issue a new one if you want to stay on the free plan.
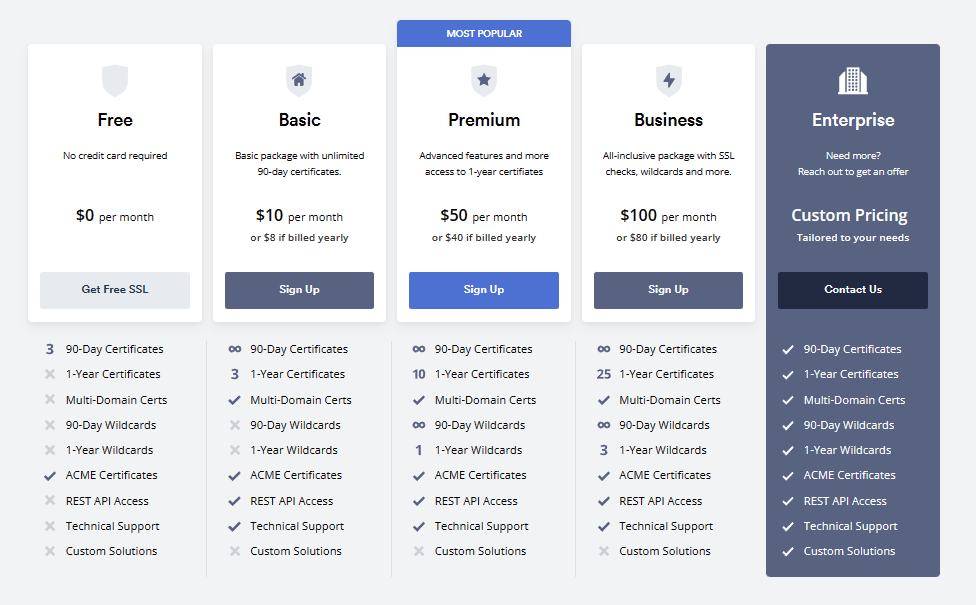
If you want to remove this hassle of renewing the certificate, you can go for one of their paid plans. They offer multiple free plans in both monthly and yearly packages. Choose the one that suits your business. The free offer is like a trial period before getting the service.
The paid plans have some special perks as well. You can use the REST API to issue/renew a certificate automatically. Also, you can help with premium support for premium plans.
Pricing: Lets Encrypt
As a non-profit organization, Lets Encrypt is completely free. Also, having giant companies like Mozilla and AWS as regular fundraisers can operate free forever. However, the free plan comes in a complex way, as you need more flexibility than ZeroSSL.
Verdict: Let’s Encrypt is free for all and forever. If you can install this on your site, you don’t have to worry again. However, though ZeroSSL revoking the free SSL after 90 days of manually renewing is doable, the paid plans keep everything automatic.
Validity of Certificate
Validity: ZeroSSL
ZeroSSL has a free SSL, but it’s only valid for a while. Even in their paid plans, you will get the certificate only for 1 year. However, you can renew the certificate after 90 days to the paid plan. The paid plans usually renew automatically, but free plans need manual verifications.
Validity: LetsEncrypt
Let’s Encrypt SSL is valid for 90 days; however, you can set up automatic renewal for that while installing. Or if you can manually renew every 90 days.
Verdict: Both ZeroSSL and Lets Encrypt have the same validation period.
Domain Verification
Website owners have to do domain verification to install the SSL certificate. You have multiple ways to do that, such as a DNS record or mostly by uploading a file.
Domain Verification: ZeroSSL
ZeroSSL has both the common method like adding a DNS record and uploading an HTTP file to the root folder. Additionally, they offer email verification, which is much easier and quicker.
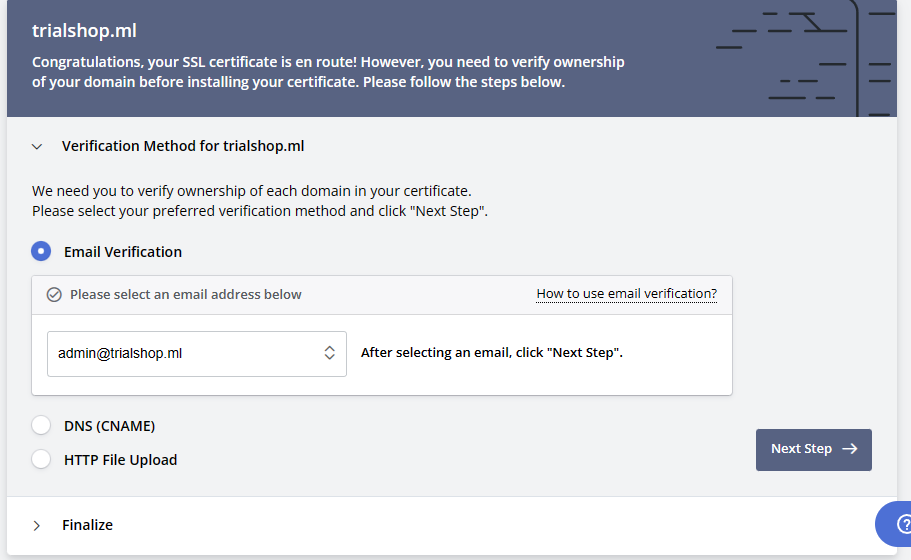
In the email verification, you don’t need domain access. Just a valid email under the domain name is enough.
Domain Verification: Let’s Encrypt
You can install the Let’s Encrypt certificate using DNS editing or file uploading to the main server. These are automatically done during the installation using SSH. However, in both cases, you must have access to the domain/server panel.
Verdict: ZeroSSL has an extra verification option, which is more suitable than the Let’s Encrypt Verification method.
Limitations
ZeroSSL: Limitations
The limitation works differently according to plans for ZeroSSL. The free plans will have 3 SSL for 90 days. But if you get their basic plans, they will provide you with unlimited certificates for 90 days.
Also, if you have acquired the SSL on the paid ACME plans on ZeroSSL, you will get an automatic unlimited renewal.
Let’s Encrypt: Limitations
Let’s Encrypt allows unlimited issuing and renewal of certificates. However, they have a fair use policy to let everyone use the technology. You will be able to issue 50 certificates per week per domain. They have some other limitations, which are quite high, and mostly, you will not hit the threshold.
Verdict: Both CA have their limitations on the free plans, but both are manageable for general users.
Multi-domain Certifications
Multi-domain certification means having one certificate for several domains. Usually, this is also known as Subject Alternative Name (SAN) certificate.
Multi-domain Certifications: ZeroSSL
ZeroSSL supports Multi-domain certification, but you have to get their paid plan. The free plan doesn’t include this feature.
Multi-domain Certifications: Let’s Encrypt
Let’s Encrypt offers this feature on the free plan, which will renew the certification as long as you follow the Fairplay limit.
Verdict: Though both CA support Multi-domain, Lets Encrypt also allows it in a free version.
Wildcard Certification
The wildcard is different from Multi-domain certification. In comparison, Multi-domain certification allows you to secure multiple domains under 1 SSL wildcard, including all subdomains and email security.
Wildcard: ZeroSSL
ZeroSSL allows Wildcard Certification only in the paid plans. Also, you will get the wildcard SSL only for 90 days. You can renew the SSL automatically with ACME API. The only drawback is you won’t get this feature in the free plan.
Wildcard: Let’s Encrypt
Unlike ZeroSSL, they allow free use of the wildcard certification. This certificate also expires every 90 days, with the ability to renew it.
Verdict: Both CA have the feature of a wildcard; whereas ZeroSSL requires a paid subscription, Let’s Encrypt does it for free.
Technical Support
Although SSL/TLS certification is automated, you might find yourself in a confusing situation. Technical support is a must when you can’t solve a problem alone. Let’s look at these two CA’s support systems.
Technical Support: ZeroSSL
Although you won’t get direct support for the free plan, ZeroSSL, being paid service, has a lot of technical support channels. You can read their detailed documentation or contact them through their Contact Form.
Technical Support: Lets Encrypt
Though they have useful documentation being a free Certificate Authority, but it doesn’t offer any technical support. However, you can join their community forum and post your problem there. Either an admin or another user might answer your solution.
Verdict: ZeroSSL has better Technical support than Let’s Encrypt.
Conclusion: ZeroSSL vs Lets Encrypt
If you read through the article till now, you get an idea of how both certificate authority works. Let’s Encrypt is a free, forever solution for everyone. You can choose and stick with it if you don’t want to pay for an SSL certificate.
However, this is much more complicated to start with for a beginner. You need a high level of knowledge to install this manually on a server or have compatibility with your cPanel.
ZeroSSL, on the other hand, has a limitation on the free plan but better UI and flexible features. You can also get support from the technical team if something goes wrong. That being said, ZeroSSL is a better choice, in my opinion.
